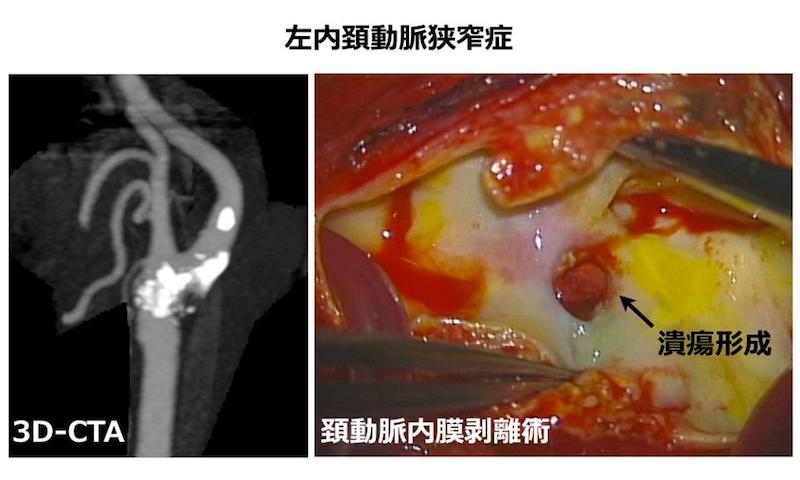
近年、わが国でも増加している動脈硬化による頚動脈狭窄症は、一過性脳虚血発作(TIA)、一過性黒内障、脳梗塞などを招く疾患として注目されています。しかし、頚動脈狭窄症は脳梗塞などをきたす以前から認知機能を低下させることが最近の研究で明らかにされつつあります。
今回、われわれは、無症候性の頚動脈狭窄症(70%以上)を有する15例で頚動脈内膜剥離術の前後に高次脳機能検査(RBANS)を実施したところ、術前、総スコアおよび即時記憶、言語、注意の3つの指標が低下していること、術後にこれらの指標が有意に改善することを明らかにしました。
Takaiwa A et al. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 2013 Jan 30 [Epub ahead of print)
詳細は以下のURLをご参照下さい。
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23361637
This study was conducted to determine if patients with asymptomatic carotid artery stenosis show cognitive function decline, and if they experience any changes in cognitive function after carotid endarterectomy (CEA). Cognitive function was examined in 15 patients (12 males and three females, 70.0±6.5 years) with asymptomatic carotid artery stenosis before and 3 months after CEA. Cognitive function was assessed with the Repeatable Battery for the Assessment of Neuropsychological Status (RBANS), two subtests of the Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale-Revised (WAIS-R 2 subtests), and the Japanese version of National Adult Reading Test (JART). The patients’ average scores were compared with the normal average by one-sample t-tests, and the before and after scores were compared with paired t-tests. Changes in each patient were calculated from difference before and after CEA using 95 % confidence intervals. Before surgery, patients showed significant cognitive decline in RBANS total scale and immediate memory, language, and attention. At 3 months after CEA, the total scale and the immediate memory were not significantly different from the normal average. The average total scale score, the immediate memory and attention, and the WAIS-R 2 subtests scores were increased after treatment. Changes in each patient were calculated from the scores before and after CEA. At 3 months after CEA, the rate of increase in RBANS scores were 60.0 % of the patients for immediate memory, 26.7 % for visuospatial/constructional, 33.3 % for language and attention, 26.7 % for delayed memory, 47.7 % for total scale and 26.7 % for WAIS-R 2 subtests. Thus, so-called asymptomatic patients exhibit mild cognitive impairment before surgery, but after CEA, patients recover normal memory abilities.Our findings of mild cognitive dysfunction in asymptomatic patients suggest that they might be symptomatic after all.