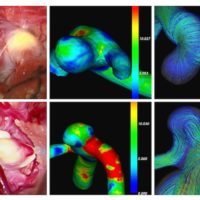
当科の柏崎大奈先生の頚動脈狭窄症と慢性腎機能不全との関連に関する論文が、Journal of Stroke and Cerebrovascular Diseases誌に掲載されました。反対側頚動脈病変(オッズ比 4.5)、不安定プラーク(オッズ比 3.3)が頚動脈手術(CEA/CAS)の症例で腎機能障害を合併するリスクが高く、不安定プラークの存在はその後も腎機能が悪化するリスクが高いことが判明しました。以前にも冠動脈疾患についても同様の結果を報告させていただきましたが、われわれの体に潜む慢性炎症が全身の臓器障害の引き金になることを強く示唆しています。
A Voyage to Depth of Neuroscience Vol. 69
Unstable Carotid Plaque as a Phenotype of Chronic Systemic Inflammation Enhances Renal Insufficiency.
Kashiwazaki D, Maruyama K, Yamamoto S, Saito H, Akioka N, Kuwayama N, Noguchi K, Kuroda S.
J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2020 Feb 21 [Epub ahead of print]
PMID: 32093991
Abstract
PURPOSE: Chronic systemic inflammation is prevalent in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) and is linked to the development of cerebrovascular disease. In this study, we explored the association between the unstable plaques and preoperative CKD in patients who underwent carotid endarterectomy (CEA)/carotid artery stenting (CAS). Furthermore, this study also aimed to explore whether there is a difference in the aggravation of renal function with the presence of stable or unstable plaques.
PATIENTS AND METHODS: The study included 90 patients who underwent CEA/CAS for carotid artery stenosis. Multivariate analysis was performed to determine the risk factors for CKD. Kaplan-Meier estimation was employed to evaluate the aggravation of renal function following CEA/CAS.
RESULTS: Multivariate analysis revealed that contralateral carotid occlusive disease (odds ratio [OR], 4.45; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.36-14.6), and T1 high-intensity carotid plaque (OR, 3.26; 95% CI, 1.2-8.86) were independent factors of CKD. Kaplan-Meier estimation demonstrated a higher aggravation of renal function in the T1 high-intensity group compared to those in the iso-intensity (P =.03). Following CEA/CAS, the time until aggravation of renal insufficiency was 12.0 ± 9.4 months in the T1 high-intensity group and 24.5 ± 9.6 months in the iso-intensity group (P =.03).
CONCLUSIONS: This study demonstrated that contralateral carotid artery stenosis and T1 high-intensity plaques are more frequently observed in patients with CKD. T1 high-intensity carotid plaque is well linked to CKD development in future.