当科の堀 聡先生の研究成果がJournal of Stroke and Cerebrovascular Disease誌に掲載されました。
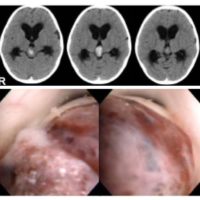
不安定プラークを有する頚動脈高度狭窄症の患者さんは、大脳深部の微小出血(microbleeds)を有意に高率に有していることが判明しました(P=0.009, OR=5.38, 95% CI= 1.51-21.0)。全身に潜在する慢性炎症が大〜中血管のみならず小血管にも大きな影響を及ぼしていることを強く示唆するデータです。
A Voyage to Depth of Neuroscience Vol. 61
Dr. Satoshi Hori, one of our staffs, published his research data on the relationship between unstable carotid plaque and microbleeds in the brain in Journal of Stroke and Cerebrovascular Disease.
Hori S, Hori E, Shibata T, Umemura K, Okamoto S, Kubo M, Horie Y, Kuroda S.
Correlation Between Cerebral Microbleeds and Vulnerable Plaque in Patients with Severe Carotid Artery Stenosis; Comparative Magnetic Resonance Imaging Study.
J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2019 Jul 27 [Epub ahead of print]
Goal: There are an increasing idea that the inflammation contributes to vasculardiseases in various organs. The pathogenesis of both cerebral small vessel diseasesuch as cerebral microbleeds and carotid plaque may be associated with chronic inflammation. This study was aimed to evaluate the correlation between microbleeds and carotid plaque characteristics.
Materials and Methods: This study enrolled 85 patients who underwent surgical/endovascular treatments for carotid artery stenosis between January 2009 and July 2016. Their clinical data were precisely analyzed. T2*-weighted magnetic resonance (MR) imaging was performed to detect the
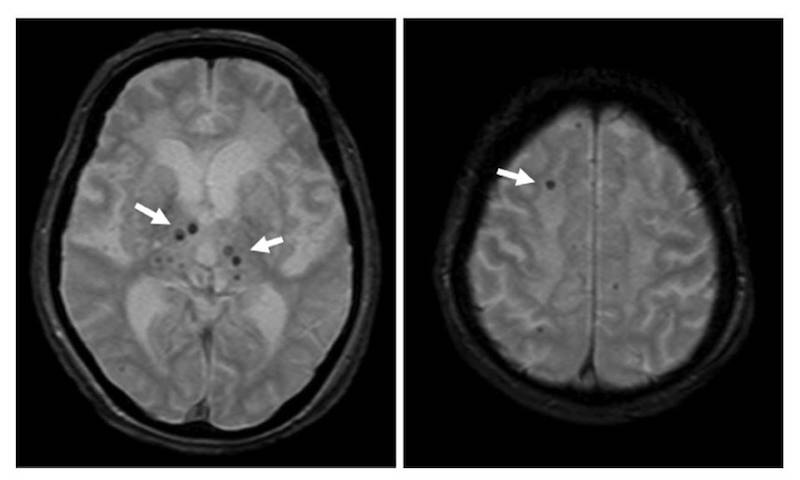
cerebral microbleeds. The carotid plaque with high signal intensity on T1-weighted MR imaging was categorized into vulnerable plaque.
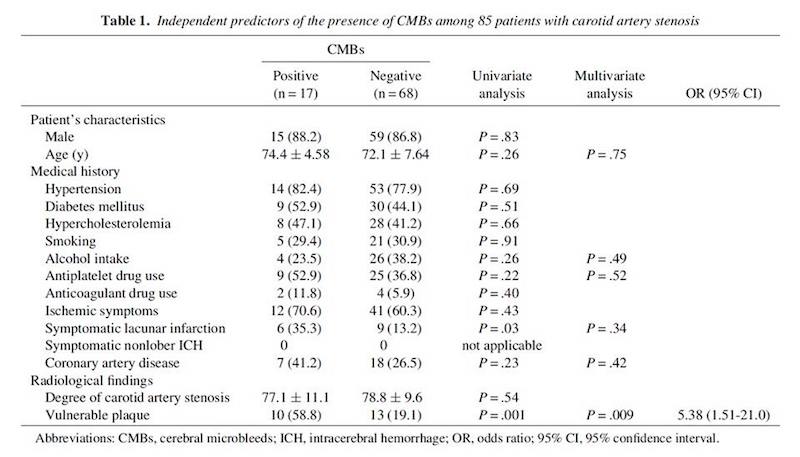
Findings: The microbleeds was detected in 17 of 85 (20%). The prevalence of vulnerable carotid plaque and previous symptomatic lacunar infarction was significantly greater in the patients with microbleeds than in those without (P = .001 and P = .03, respectively). Multiple logistic regression analysis showed that the vulnerable plaque was significantly
associated with the presence of microbleeds when adjusted for age, alcohol intake, antiplatelet drug use, the presence of previous symptomatic lacunar infarction, and coronary artery disease (P = .009, OR = 5.38, 95% CI = 1.51-21.0). Conclusions: These findings suggest the correlation between microbleeds and vulnerable plaque in patients with severe (>70%) carotid artery stenosis. Systemic, chronic inflammation may play a key role in both small and large arteries’ disease of the brain. The knowledge may be valuable to fully understand the entity of cerebrovascular diseases as one of systemic, chronic inflammation.