【パーキンソン病に対する深部脳刺激療法】
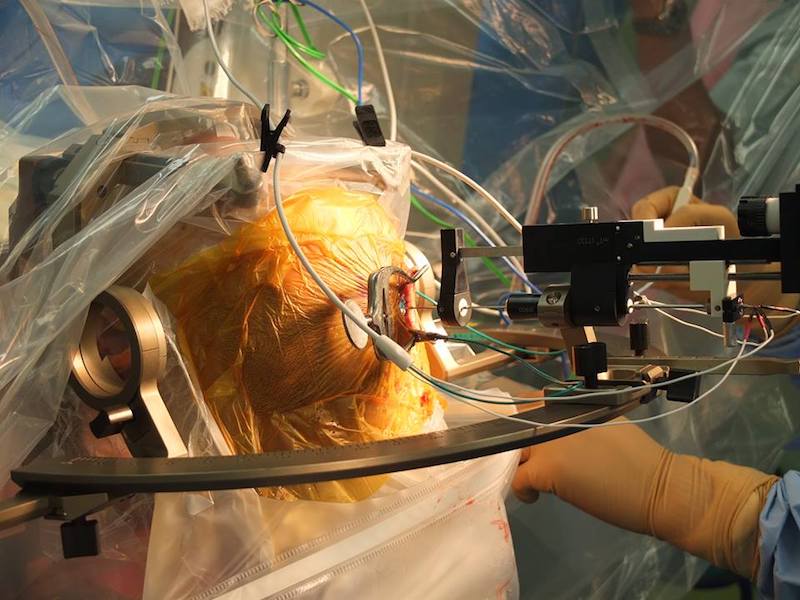
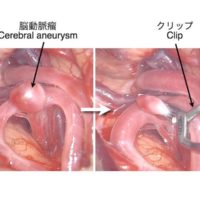
パーキンソン病は振戦や固縮、歩行障害などを主徴とする神経疾患で、中脳黒質に存在してドーパミンを産生する神経細胞の変性が疾患の本態です。薬物療法が基本ですが、治療抵抗性を示す症例の中には、深部脳刺激療法(deep brain stimulation; DBS)が劇的に神経症状を改善させることが知られています。当科は北陸随一のDBSの治療経験を有しています。
今回、われわれは、RBANSなどの神経心理テストがパーキンソン病の患者さんに存在している高次脳機能障害を鋭敏に検出できること、DBSによる運動機能の改善が良好な症例では高次脳機能も改善することを見出し報告させていただきました。この研究は、富山大学の脳神経外科医、神経内科医、言語聴覚士の真摯なる協力によって成し遂げられました。ぜひ、ご一読下さい。
Asahi T, Nakamichi N, Takaiwa A, Kashiwazaki D, Koh M, Dougu N, Takashima S, Tanaka K, Kuroda S.
Impact of Bilateral Subthalamic Stimulation on Motor/Cognitive Functions in Parkinson’s Disease.
Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 2014 May 29. [Epub ahead of print]
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24872253
It is still unclear whether deep brain stimulation targeted to the bilateral subthalamic nucleus (STN-DBS) affects cognitive function in Parkinson’s disease (PD). This prospective study was aimed to systemically evaluate the impact of bilateral STN-DBS on motor and cognitive functions in patients with PD. This study included totally 11 Japanese patients with medically intolerant PD. Neurological and cognitive status was precisely evaluated before and 1 year after bilateral STN-DBS, using unified Parkinson’s disease rating scale (UPDRS), levodopa equivalent doses, mini-mental state examination (MMSE), Japanese adult reading test (JART), repeatable battery for the assessment of neuropsychological status (RBANS), and Wechsler adult intelligence scale-revised (WAIS-R). Preoperative RBANS and WAIS-R identified cognitive dysfunction that could not be detected by MMSE and JART. Before surgery, PD patients had significantly impaired immediate memory and attention. Motor function significantly improved 1 year after bilateral STN-DBS. Bilateral STN-DBS did not affect any score on cognitive examinations. However, postoperative improvements of total score on RBANS and performance intelligence quotient (PIQ) scores on WAIS-R were closely related to those of UPDRS part III off (R2 = 0.61, P < 0.01; R2 = 0.39, P < 0.05, respectively). These findings strongly suggest that bilateral STN-DBS may significantly improve cognitive function in a certain subgroup of patients whose therapeutic effects on motor function are prominent.